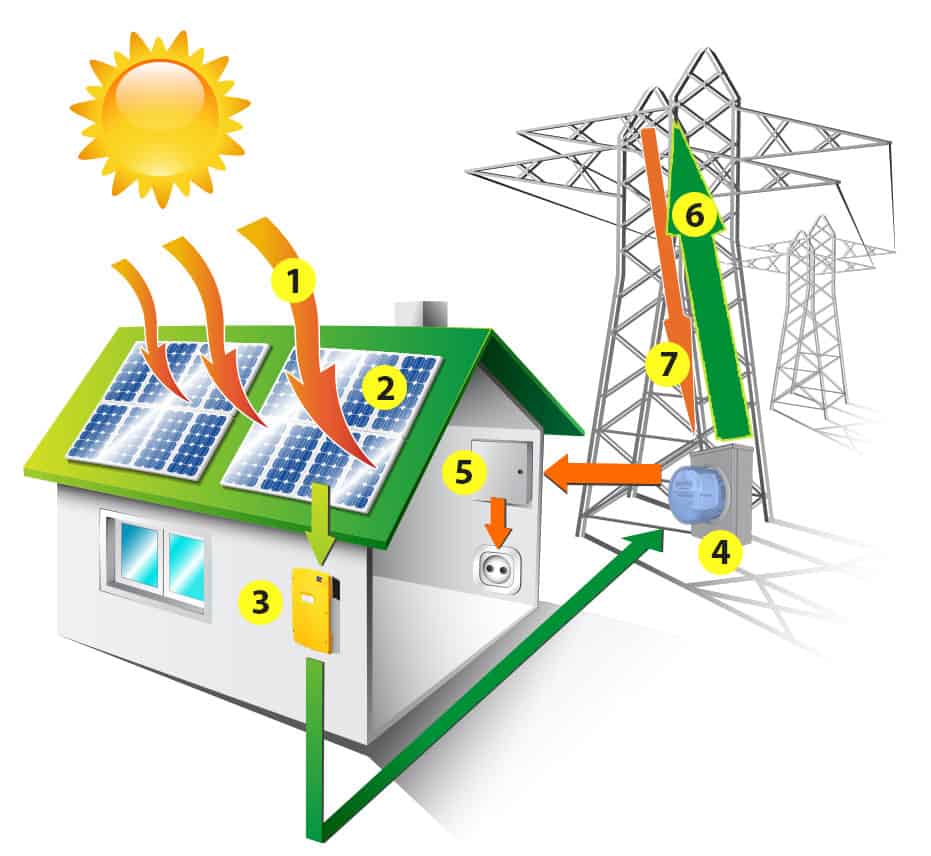
1. The Source
Sun provides free energy every day. Light from the sun hits solar panels with photons (particles of sunlight) and create energy.
2. Solar Panels
Solar panels absorb light (reflected and diffused, as well as direct) and convert photons into electrons of Direct Current (DC) electricity using a semi conducting substance, usually silicon. There are three (3) types of PV solar panels – monocrystalline silicon cells, polycrystalline cells or amorphous silicon cells. Your annual energy usage determines how many panels need to be provided.
3. Inverter
The DC power accumulated from solar panels is sent to an inverter, where it is converted into Alternating Current (AC) power so that the electricity is compatible with household appliances.
4. Net Meter
The net meter replaces the utility meter and records the net amount of energy generated through the PV Solar system. When you are generating more electricity than you are using the overage power is sent onto the grid, spinning your meter backwards and accumulating credits with the utility company. This helps to offset the cost of your electricity usage at night or on cloudy days when your system is not producing electricity, saving you money!
5. Electrical Panel
The electrical panel often called a breaker box receives AC power from the inverter. This AC power is now ready to be utilized in your home.
6. Excess AC energy
With net metering over produce / unused solar electricity is sent back into the grid for credits and it can be used by someone else. You will be paid for the surplus electricity exported to the grid.
7. Electricity sent from utility
Your home remains connected to the utility grid to supply you with electricity. When you need more power than your solar system produces or when you are not producing solar power at night your credits are utilized and electricity flows back from the grid into your home.